Jun 20, 2009
BDC Interview Questions
ABAP BDC Interview Questions
1 What should be the approach for writing a BDC program?
Ans.: 1. Analysis the Data.2. Generate SAP structure.3. Develop transfer program 4. Create sequential file. 5. Create batch input program. 6. Process batch input data
2 What is the alternative to batch input session?
Ans. : Call transaction & call dialog
What are the steps in a BDC session ?
The first step in a BDC session is to identify the screens of the transaction that the program will process. Next step is to write a program to build the BDC table that will be used to submit the data to SAP. The final step is to submit the BDC table to the system in the batch mode or as a single transaction by the CALL TRANSACTION command.
3 What are the problems in processing batch input sessions? How is batch input process different from processing on line?
Ans.: Sessions cannot be run in parallel and not fast.
4 What do you do when the system crashes in the middle of a BDC batch session?
Check no. of records already updated and delete them from input file and run BDC again.
5 What do you do with errors in BDC batch session?
Analysis and correct input file format and entries in internal table BDCDATA.
6 WHAT are the commands that allow you to process sequential file? And what is their syntax?
Ans :- READ DATASET (reading) and TRANSFER (writing)
OPEN DTASET (dataset name) for(input/output appending) in (binary text ) mode at POSITION (position) MESSAGE(field)
READ DATASET (dataset name ) INTO (field)
CLOSE DATASET (dataset name)
DELETE DATASET (dataset name)
TRANSFER (field) to (dataset name)
7 What is the process for transferring data from legacy system to SAP?
Ans :- FTP file transfer, Manufacturer –specific field transfer NFS(network file system)/BDC.
8 Explain the process to transfer a record to a dataset?
Ans :- TRANSFER (field) to (dataset name).
9 Why batch input?
Ans :- To input a large amount of information at off peak times.
10 Can data be put directly into the database?
Ans :- No, only after the data has been entered via transaction.
11 Explain at high level, the batch input process?
Ans :- Batch data is placed into queues called batch input sessions , then placed into the application programs for maintenance into the database.
12 What are the function modules associated with batch input?
Ans :- BDC_OPEN_GROUP , BDC_CLOSE_GROUP , BDC_INSERT
13 What is the structure of the BDC table?
Ans :- Program/Dynpro/start/field name/ field content.
14 Write out a coding example for filling a BDC Table.
Ans :- FORM (NAME)
REFEESH (bdc table)
CLEAR (bdc table)
MOVE (program name) to (bdc table)-PROGRAM
(number1) TO (bdc table)-DYNPRO
‘X’ TO (bdc table)-DYNBEGIN
APPEND (bdc table)
CLEAR(bdc table)
MOVE: (field1) TO (bdc table)-FNAM
(field2) TO (bdc table)-FVAL
APPEND (bdc table)
15How do you find the transaction number, program number and field names?
Ans :- Transaction no.,program no. – System -> status
Field names - F1, Technical help
16 What are the processing modes for Batch Input?
Ans :- Process on screen(foreground) , Display errors only and process in the background
17What are the available OK Codes that can be utilized during batch input processing?
Ans :- /n – terminates current batch input transaction and marks as incorrect.
/bdel – delete current batch input transaction from session.
/bend – terminate batch input processing and mark session as incorrect.
/bda – change display mode to process the session on screen instead of displaying only errors.
/bde – change display mode to display only errors instead of processing the session on the screen.
18 What is the effect of the BDC_CURSOR field name in the BDC table?
Ans :- You can set the cursor and enter as a corresponding field value the name of the field on which the cursor is to be positioned .
19 How many types of BDCs you have done?
21Why you choose Call transaction and/or session method?
Call transaction is mainly used when you want to update the database using a single transaction , you can also update the database in asynchronous mode, where as session is used to perform huge database updations using more than one transaction and which will last for a long time.
22 How you trap errors in call Transaction
Errors while updating the database using call transaction technique are trapped using a structure bdcmsgcall, whose field msgtyp become ‘e’ when an error record is encountered. Those records are formatted using format_message function call in the desired format and stored in an internal table for listing of all error records in one shot.
23 What are different types of Update modes
In BDC’s we have two types of updation modes – 1) Synchronous 2) Asynchronous
24 What is main difference between session method and LSMW
In the context of session method,
the method of updating is “Batch Input” ,
we require a program to be coded,
But in the context of LSMW method,
The methods of updating
using “Batch Input/Direction Input”
from an IDOC,
from a BAPI structure.
No source code is required, the complete operation is performed in 16 steps sequence
25 What is main difference between CATT and LSMW
Using LSMW you can update any kind of data but no changes to database are allowed, where as CATT tool can update only master data, which also allows changes to the master data and also a significant testing of data is possible
26 What is BDC and How you use it?
BC Basis Components--ABAP workbench--BC Basis Programming interfaces--Data transfer
During data transfer, data is transferred from an external system into the SAP R/3 System. •Transfer data from an external system into an R/3 System as it is installed. •Transfer data regularly from an external system into an R/3 System.
Example: If data for some departments in your company is input using a system other than the R/3 System, you can still integrate this data in the R/3 System. To do this, you export the data from the external system and use a data transfer method to import it into the R/3 System.
Batch input with batch input sessions : Data consistency check with the help of screen logic.
With the batch input method, an ABAP program reads the external data that is to be entered in the R/3 System and stores the data in a "batch input session". The session records the actions that are required to transfer data into the system using normal SAP transactions.
When the program has generated the session, you can run the session to execute the SAP transactions in it. You can explicitly start and monitor a session with the batch input management function (by choosing System ® Services ® Batch input), or have the session run in the background processing system.
Use the BDC_OPEN_GROUP function module to create a new session. Once you have created a session, then you can insert batch input data into it with BDC_INSERT. Use the BDC_INSERT function module to add a transaction to a batch input session. Use the BDC_CLOSE_GROUP function module to close a session after you have inserted all of your batch input data into it.
What is Dataset and how you use it?
ABAP/4 provides three statements for handling files:
The OPEN DATASET statement opens a file.
The CLOSE DATASET statement closes a file.
The DELETE DATASET statement deletes a file.
To open a file for read access, use the FOR INPUT option of the OPEN DATASET statement
To open a file for write access, use the FOR OUTPUT option of the OPEN DATASET statement
To open a file for appending data to the file, use the FOR APPENDING option of the OPEN DATASET statement
To process a file in binary mode, use the IN BINARY MODE option of the OPEN DATASET statement
To process a file in text mode, use the IN TEXT MODE option of the OPEN DATASET statement
To open a file at a specific position, use the AT POSITION option of the OPEN DATASET statement
When you work with the operating systems UNIX or WINDOWS NT, you can send an operating system command with the statement OPEN DATASET. To do so, use the option FILTER
To receive the operating system message after trying to open a file, use the MESSAGE option of the OPEN DATASET statement
To close a file on the application server, use the CLOSE DATASET statement
To delete a file on the application server, use the DELETE DATASET statement
To write data to a file on the application server, use the TRANSFER statement
To read data from a file on the application server, use the READ DATASET statement.
36 Give real time work done by u in BDC ? Transactions used ? parameters passed with functions.
37 will ask u for screen no's and dynpro names for BDC that u say u have done.
39 Which technical field in the BDCDATA table holds the last cursor position?
41 What is true about the LSMW: (choose correct option/s)
Part of the SAP system
Processes hierarchical data files (header and position)
Needs a source field for every target field
44 How do you read a LOCAL sequential file?
45 How do you write a sequential file?
46 How do you send the BDCDATA table in a Call Transaction statement?
47 What loop do you code for a READ DATASET statement?
51 What are the steps in a BDC session ?
The first step in a BDC session is to identify the screens of the transaction that the program will process. Next step is to write a program to build the BDC table that will be used to submit the data to SAP. The final step is to submit the BDC table to the system in the batch mode or as a single transaction by the CALL TRANSACTION command.
52 How do you find the information on the current screen ?
Status command from any menu.The information on the current screen can be found by System
53 How do you save data in BDC tables ?
The data in BDC tables is saved by using the field name ‘BDC_OKCODE’ and field value of ‘/11’
54 What is the last entry in all BDC tables ?
In all BDC tables, the last entry is to save the data by using the field name BDC_OKCODE and a field value of ‘/11’.
55 What is a multiple line field ?
A multiple line field is a special kind of field which allows the user to enter multiple lines of data into it.
56 How do you populate data into a multiple line field ?
To populate data into a multiple line field, an index is added to the field name to indicate which line is to be populated by the BDC session (Line index ).
57 Write the BDC table structure.
BDC table structure
FIELD TYPE DESCRIPTION
Program CHAR(8) Program name of transaction
DynPro CHAR(4) Screen number of transaction
DynBegin CHAR(1) Indicator for new screen
Fnam CHAR(35) Name of database field from
Screen
Fval CHAR(80) Value to submit to field
58 Does the CALL TRANSACTION method allow multiple transactions to be processed by SAP ?
No. The CALL TRANSACTION method allows only a single transaction to be processed by SAP.
59 Does the BDC_INSERT function allow multiple transactions to be processed by SAP ?
Yes.
60 What is the syntax for ‘CALL TRANSACTION’ ?
CALL TRANSACTION trans [ using bdctab MODE mode ].
Three possible entries are there for MODE.
A - show all screens
E - show only screens with errors
N - show no screens
Which mode of ‘CALL TRANSACTION’ method allows background processing ?
N is the only mode that allows background processing.
61 Is it possible to use ‘CALL TRANSACTION’ without a BDC table ?
Yes, it is possible to use ‘CALL TRANSACTION’ without a BDC table. In such case, the current program is suspended, the transaction specified is brought up, and a user must enter the data into the screens.
62 What is TCODE ?
TCODE is the transaction code for the transaction that should be used to process the data in the BDC table being inserted.
63 What are the function modules that need to be called from BDC program to submit the transactions for processing ?
- BDC_OPEN_GROUP
- BDC_INSERT
- BDC_CLOSE_GROUP
64 How many sessions will be opened using BDC_OPEN_GROUP ?
Only one session can be created using the BDC_OPEN_GROUP functon.
65 What is ‘BATCH INPUT’ or ‘BDC’ ?
The SAP system offers two primary methods (BDC SESSION METHOD, CALL TRANSACTION METHOD) for transferring data into the system from other systems and Non-SAP systems. These two methods are collectively called as ‘BATCH INPUT’ or ‘Batch Data Communication’ (BDC).
66 What are the advantages in Batch Input ?
The Batch Input ensures Data integrity.
No manual interaction is required during Data transfer.
67 What is the functionality of ‘Classical Batch Input’ ?
In ‘Classical Batch Input’ an ABAP/4 program reads the external data that is to be entered in the SAP system and stores the data in a Batch Input session. This session stores the actions that are required to enter your data using normal SAP transactions.
68 Which Function Modules are used in ‘Classical Batch Input’ ?
BDC_OPEN_GROUP , BDC_INSERT, BDC_CLOSE_GROUP.
69 What is Synchronous Database update ?
During the processing no transaction is stored until the previous transaction has been written to the Database. This is called Synchronous Database update.
70 What are the differences between CALL TRANSACTION and BATCH INPUT SESSION ?
- The most important aspects of the batch session interface are:
- Asynchronous processing
- Transfers data for multiple transactions
- Synchronous database update
During processing, no transaction is started until the previous transaction has been written to the database.
- A batch input processing log is generated for each session
- Sessions cannot be generated in parallel
The most important aspects of the CALL TRANSACTION USING interface are:
- Synchronous processing
- Transfers data for a single transaction
- Synchronous and asynchronous database updating both possible
The program specifies which kind of updating is desired.
- Separate LUW for the transaction
The system performs a database commit immediately before and after the CALL TRANSACTION USING statement.
No batch input processing log is generated
71 What are the types of Batch Input ?
Classical Batch Input
Call Transaction
Call Dialog
72 What is BDC_OKCODE ?
The command field is identified by a special name in batch input called BDC_OKCODE. This name is constant and always identifies the command field.
73 How can we execute a function in a BDC session ?
We can execute a function in a transaction by entering the function code or function key number in the command field of an SAP session. A function key number must be prefixed with the / (slash) character. A function code must be prefixed with the = character.
Example:
BDCDATA-FNAM = 'BDC_OKCODE'
BDCDATA-FVAL = '=UPDA'
74 How can we position the cursor on a particular field ?
BDCDATA-FNAM = ‘BDC_CURSOR’
BDCDATA-FVAL =
75 Who are Dialog users and who are Background users ?
Dialog users are normal interactive users in the SAP system. Background users are user master records that are specially defined for providing authorizations for background processing jobs.
76 What is the use of BDC_INSERT ?
We add a transaction to a Batch Input Session by using this function.
77 What are the update modes in CALL TRANSACTION ?
S : Synchronous
A : Asynchrnous
L : Local
78 What does the message parameter indicates ?
The message parameter indicates there all system messages issued during a CALL TRANSACTION are written into the internal table. The internal table must have the structure of BDCMSGCOLL.
79 What is Direct Input ?
To enhance the batch input procedure, the system offers the direct input technique especially for transferring large amount of data. This technique doesn’t create sessions but stores the data directly. The direct input programs must be executed in the back ground only. To maintain and start these programs, use program RBMVSHOW or the transaction BMVO.
80 What are the features of Recording Function ?
recording transaction runs
creating batch input sessions from the recorded transaction runs.
Generating a batch input program from the recorded data.
81 What is synchrnous database update ?
During the processing, no transaction is stored until the previous transaction has been written to the database. This is called Synchronous database update.
82 How do you set up batch process?
Data analysis: Analyze the data that is to be transferred to the SAP System.
||
Generate SAP structures: Generate SAP data structures for incorporation into your data export program.
||
Develop transfer program: You can write the program in ABAP/4 or as an external program.
||
Create sequential file: Export the data that is to be transferred, to a sequential file.
||
Create batch input program: ABAP/4 batch input program that will read the data to be transferred from the sequential file.
||
Process batch input data: Process the data and add it to the SAP System. You can do this either by:
batch-input session method or Call transaction method.
||
Analyse results: Check that all data has been successfully processed.
||
Analyse Error session: Correct and re-process erroneous data.
83 Where do you use BDC?
transferring data from another system when you install your SAP System
regularly transferring data that is captured by a non-SAP system in your company into the SAP System. Assume, for example, that data collection in some areas of your company is still performed by a non-SAP system. You can still consolidate all of your data in the SAP System by exporting the data from the other system and reading it into the SAP System with batch input.
You can also use batch input to transfer data between two R/3 Systems. However, there are more direct methods for doing this, such as RFC (remote function calls).
84 What has to be done to the packed fields before submitting to a BDC session?
Declare these fields in the internal table as characters and the length of the field should be same as the field length of the field's data element. This internal table is used to hold the data fetched from the sequential file using WS-upload function module
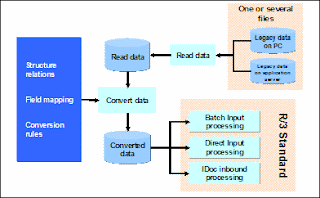
What is LSMW
The LSMW is a cross-application component (CA) of the SAP R/3 System.
The tool has interfaces with the Data Transfer Center and with batch input and direct input processing as well as standard interfaces BAPI and IDoc in R/3.
The LSMW comprises the following main functions:
Read data (legacy data in spreadsheet tables and/or sequential files).
Function Read data replaces and enhances functions Spreadsheet interface and Host interface of LSMW version 1.0. You can use any combination out of PC and server files now.
Convert data (from the source into the target format).
Import data (to the database used by the R/3 application).
TCODE - LSMW
1 What should be the approach for writing a BDC program?
Ans.: 1. Analysis the Data.2. Generate SAP structure.3. Develop transfer program 4. Create sequential file. 5. Create batch input program. 6. Process batch input data
2 What is the alternative to batch input session?
Ans. : Call transaction & call dialog
What are the steps in a BDC session ?
The first step in a BDC session is to identify the screens of the transaction that the program will process. Next step is to write a program to build the BDC table that will be used to submit the data to SAP. The final step is to submit the BDC table to the system in the batch mode or as a single transaction by the CALL TRANSACTION command.
3 What are the problems in processing batch input sessions? How is batch input process different from processing on line?
Ans.: Sessions cannot be run in parallel and not fast.
4 What do you do when the system crashes in the middle of a BDC batch session?
Check no. of records already updated and delete them from input file and run BDC again.
5 What do you do with errors in BDC batch session?
Analysis and correct input file format and entries in internal table BDCDATA.
6 WHAT are the commands that allow you to process sequential file? And what is their syntax?
Ans :- READ DATASET (reading) and TRANSFER (writing)
OPEN DTASET (dataset name) for(input/output appending) in (binary text ) mode at POSITION (position) MESSAGE(field)
READ DATASET (dataset name ) INTO (field)
CLOSE DATASET (dataset name)
DELETE DATASET (dataset name)
TRANSFER (field) to (dataset name)
7 What is the process for transferring data from legacy system to SAP?
Ans :- FTP file transfer, Manufacturer –specific field transfer NFS(network file system)/BDC.
8 Explain the process to transfer a record to a dataset?
Ans :- TRANSFER (field) to (dataset name).
9 Why batch input?
Ans :- To input a large amount of information at off peak times.
10 Can data be put directly into the database?
Ans :- No, only after the data has been entered via transaction.
11 Explain at high level, the batch input process?
Ans :- Batch data is placed into queues called batch input sessions , then placed into the application programs for maintenance into the database.
12 What are the function modules associated with batch input?
Ans :- BDC_OPEN_GROUP , BDC_CLOSE_GROUP , BDC_INSERT
13 What is the structure of the BDC table?
Ans :- Program/Dynpro/start/field name/ field content.
14 Write out a coding example for filling a BDC Table.
Ans :- FORM (NAME)
REFEESH (bdc table)
CLEAR (bdc table)
MOVE (program name) to (bdc table)-PROGRAM
(number1) TO (bdc table)-DYNPRO
‘X’ TO (bdc table)-DYNBEGIN
APPEND (bdc table)
CLEAR(bdc table)
MOVE: (field1) TO (bdc table)-FNAM
(field2) TO (bdc table)-FVAL
APPEND (bdc table)
15How do you find the transaction number, program number and field names?
Ans :- Transaction no.,program no. – System -> status
Field names - F1, Technical help
16 What are the processing modes for Batch Input?
Ans :- Process on screen(foreground) , Display errors only and process in the background
17What are the available OK Codes that can be utilized during batch input processing?
Ans :- /n – terminates current batch input transaction and marks as incorrect.
/bdel – delete current batch input transaction from session.
/bend – terminate batch input processing and mark session as incorrect.
/bda – change display mode to process the session on screen instead of displaying only errors.
/bde – change display mode to display only errors instead of processing the session on the screen.
18 What is the effect of the BDC_CURSOR field name in the BDC table?
Ans :- You can set the cursor and enter as a corresponding field value the name of the field on which the cursor is to be positioned .
19 How many types of BDCs you have done?
21Why you choose Call transaction and/or session method?
Call transaction is mainly used when you want to update the database using a single transaction , you can also update the database in asynchronous mode, where as session is used to perform huge database updations using more than one transaction and which will last for a long time.
22 How you trap errors in call Transaction
Errors while updating the database using call transaction technique are trapped using a structure bdcmsgcall, whose field msgtyp become ‘e’ when an error record is encountered. Those records are formatted using format_message function call in the desired format and stored in an internal table for listing of all error records in one shot.
23 What are different types of Update modes
In BDC’s we have two types of updation modes – 1) Synchronous 2) Asynchronous
24 What is main difference between session method and LSMW
In the context of session method,
the method of updating is “Batch Input” ,
we require a program to be coded,
But in the context of LSMW method,
The methods of updating
using “Batch Input/Direction Input”
from an IDOC,
from a BAPI structure.
No source code is required, the complete operation is performed in 16 steps sequence
25 What is main difference between CATT and LSMW
Using LSMW you can update any kind of data but no changes to database are allowed, where as CATT tool can update only master data, which also allows changes to the master data and also a significant testing of data is possible
26 What is BDC and How you use it?
BC Basis Components--ABAP workbench--BC Basis Programming interfaces--Data transfer
During data transfer, data is transferred from an external system into the SAP R/3 System. •Transfer data from an external system into an R/3 System as it is installed. •Transfer data regularly from an external system into an R/3 System.
Example: If data for some departments in your company is input using a system other than the R/3 System, you can still integrate this data in the R/3 System. To do this, you export the data from the external system and use a data transfer method to import it into the R/3 System.
Batch input with batch input sessions : Data consistency check with the help of screen logic.
With the batch input method, an ABAP program reads the external data that is to be entered in the R/3 System and stores the data in a "batch input session". The session records the actions that are required to transfer data into the system using normal SAP transactions.
When the program has generated the session, you can run the session to execute the SAP transactions in it. You can explicitly start and monitor a session with the batch input management function (by choosing System ® Services ® Batch input), or have the session run in the background processing system.
Use the BDC_OPEN_GROUP function module to create a new session. Once you have created a session, then you can insert batch input data into it with BDC_INSERT. Use the BDC_INSERT function module to add a transaction to a batch input session. Use the BDC_CLOSE_GROUP function module to close a session after you have inserted all of your batch input data into it.
What is Dataset and how you use it?
ABAP/4 provides three statements for handling files:
The OPEN DATASET statement opens a file.
The CLOSE DATASET statement closes a file.
The DELETE DATASET statement deletes a file.
To open a file for read access, use the FOR INPUT option of the OPEN DATASET statement
To open a file for write access, use the FOR OUTPUT option of the OPEN DATASET statement
To open a file for appending data to the file, use the FOR APPENDING option of the OPEN DATASET statement
To process a file in binary mode, use the IN BINARY MODE option of the OPEN DATASET statement
To process a file in text mode, use the IN TEXT MODE option of the OPEN DATASET statement
To open a file at a specific position, use the AT POSITION option of the OPEN DATASET statement
When you work with the operating systems UNIX or WINDOWS NT, you can send an operating system command with the statement OPEN DATASET. To do so, use the option FILTER
To receive the operating system message after trying to open a file, use the MESSAGE option of the OPEN DATASET statement
To close a file on the application server, use the CLOSE DATASET statement
To delete a file on the application server, use the DELETE DATASET statement
To write data to a file on the application server, use the TRANSFER statement
To read data from a file on the application server, use the READ DATASET statement.
36 Give real time work done by u in BDC ? Transactions used ? parameters passed with functions.
37 will ask u for screen no's and dynpro names for BDC that u say u have done.
39 Which technical field in the BDCDATA table holds the last cursor position?
41 What is true about the LSMW: (choose correct option/s)
Part of the SAP system
Processes hierarchical data files (header and position)
Needs a source field for every target field
44 How do you read a LOCAL sequential file?
45 How do you write a sequential file?
46 How do you send the BDCDATA table in a Call Transaction statement?
47 What loop do you code for a READ DATASET statement?
51 What are the steps in a BDC session ?
The first step in a BDC session is to identify the screens of the transaction that the program will process. Next step is to write a program to build the BDC table that will be used to submit the data to SAP. The final step is to submit the BDC table to the system in the batch mode or as a single transaction by the CALL TRANSACTION command.
52 How do you find the information on the current screen ?
Status command from any menu.The information on the current screen can be found by System
53 How do you save data in BDC tables ?
The data in BDC tables is saved by using the field name ‘BDC_OKCODE’ and field value of ‘/11’
54 What is the last entry in all BDC tables ?
In all BDC tables, the last entry is to save the data by using the field name BDC_OKCODE and a field value of ‘/11’.
55 What is a multiple line field ?
A multiple line field is a special kind of field which allows the user to enter multiple lines of data into it.
56 How do you populate data into a multiple line field ?
To populate data into a multiple line field, an index is added to the field name to indicate which line is to be populated by the BDC session (Line index ).
57 Write the BDC table structure.
BDC table structure
FIELD TYPE DESCRIPTION
Program CHAR(8) Program name of transaction
DynPro CHAR(4) Screen number of transaction
DynBegin CHAR(1) Indicator for new screen
Fnam CHAR(35) Name of database field from
Screen
Fval CHAR(80) Value to submit to field
58 Does the CALL TRANSACTION method allow multiple transactions to be processed by SAP ?
No. The CALL TRANSACTION method allows only a single transaction to be processed by SAP.
59 Does the BDC_INSERT function allow multiple transactions to be processed by SAP ?
Yes.
60 What is the syntax for ‘CALL TRANSACTION’ ?
CALL TRANSACTION trans [ using bdctab MODE mode ].
Three possible entries are there for MODE.
A - show all screens
E - show only screens with errors
N - show no screens
Which mode of ‘CALL TRANSACTION’ method allows background processing ?
N is the only mode that allows background processing.
61 Is it possible to use ‘CALL TRANSACTION’ without a BDC table ?
Yes, it is possible to use ‘CALL TRANSACTION’ without a BDC table. In such case, the current program is suspended, the transaction specified is brought up, and a user must enter the data into the screens.
62 What is TCODE ?
TCODE is the transaction code for the transaction that should be used to process the data in the BDC table being inserted.
63 What are the function modules that need to be called from BDC program to submit the transactions for processing ?
- BDC_OPEN_GROUP
- BDC_INSERT
- BDC_CLOSE_GROUP
64 How many sessions will be opened using BDC_OPEN_GROUP ?
Only one session can be created using the BDC_OPEN_GROUP functon.
65 What is ‘BATCH INPUT’ or ‘BDC’ ?
The SAP system offers two primary methods (BDC SESSION METHOD, CALL TRANSACTION METHOD) for transferring data into the system from other systems and Non-SAP systems. These two methods are collectively called as ‘BATCH INPUT’ or ‘Batch Data Communication’ (BDC).
66 What are the advantages in Batch Input ?
The Batch Input ensures Data integrity.
No manual interaction is required during Data transfer.
67 What is the functionality of ‘Classical Batch Input’ ?
In ‘Classical Batch Input’ an ABAP/4 program reads the external data that is to be entered in the SAP system and stores the data in a Batch Input session. This session stores the actions that are required to enter your data using normal SAP transactions.
68 Which Function Modules are used in ‘Classical Batch Input’ ?
BDC_OPEN_GROUP , BDC_INSERT, BDC_CLOSE_GROUP.
69 What is Synchronous Database update ?
During the processing no transaction is stored until the previous transaction has been written to the Database. This is called Synchronous Database update.
70 What are the differences between CALL TRANSACTION and BATCH INPUT SESSION ?
- The most important aspects of the batch session interface are:
- Asynchronous processing
- Transfers data for multiple transactions
- Synchronous database update
During processing, no transaction is started until the previous transaction has been written to the database.
- A batch input processing log is generated for each session
- Sessions cannot be generated in parallel
The most important aspects of the CALL TRANSACTION USING interface are:
- Synchronous processing
- Transfers data for a single transaction
- Synchronous and asynchronous database updating both possible
The program specifies which kind of updating is desired.
- Separate LUW for the transaction
The system performs a database commit immediately before and after the CALL TRANSACTION USING statement.
No batch input processing log is generated
71 What are the types of Batch Input ?
Classical Batch Input
Call Transaction
Call Dialog
72 What is BDC_OKCODE ?
The command field is identified by a special name in batch input called BDC_OKCODE. This name is constant and always identifies the command field.
73 How can we execute a function in a BDC session ?
We can execute a function in a transaction by entering the function code or function key number in the command field of an SAP session. A function key number must be prefixed with the / (slash) character. A function code must be prefixed with the = character.
Example:
BDCDATA-FNAM = 'BDC_OKCODE'
BDCDATA-FVAL = '=UPDA'
74 How can we position the cursor on a particular field ?
BDCDATA-FNAM = ‘BDC_CURSOR’
BDCDATA-FVAL =
75 Who are Dialog users and who are Background users ?
Dialog users are normal interactive users in the SAP system. Background users are user master records that are specially defined for providing authorizations for background processing jobs.
76 What is the use of BDC_INSERT ?
We add a transaction to a Batch Input Session by using this function.
77 What are the update modes in CALL TRANSACTION ?
S : Synchronous
A : Asynchrnous
L : Local
78 What does the message parameter indicates ?
The message parameter indicates there all system messages issued during a CALL TRANSACTION are written into the internal table
79 What is Direct Input ?
To enhance the batch input procedure, the system offers the direct input technique especially for transferring large amount of data. This technique doesn’t create sessions but stores the data directly. The direct input programs must be executed in the back ground only. To maintain and start these programs, use program RBMVSHOW or the transaction BMVO.
80 What are the features of Recording Function ?
recording transaction runs
creating batch input sessions from the recorded transaction runs.
Generating a batch input program from the recorded data.
81 What is synchrnous database update ?
During the processing, no transaction is stored until the previous transaction has been written to the database. This is called Synchronous database update.
82 How do you set up batch process?
Data analysis: Analyze the data that is to be transferred to the SAP System.
||
Generate SAP structures: Generate SAP data structures for incorporation into your data export program.
||
Develop transfer program: You can write the program in ABAP/4 or as an external program.
||
Create sequential file: Export the data that is to be transferred, to a sequential file.
||
Create batch input program: ABAP/4 batch input program that will read the data to be transferred from the sequential file.
||
Process batch input data: Process the data and add it to the SAP System. You can do this either by:
batch-input session method or Call transaction method.
||
Analyse results: Check that all data has been successfully processed.
||
Analyse Error session: Correct and re-process erroneous data.
83 Where do you use BDC?
transferring data from another system when you install your SAP System
regularly transferring data that is captured by a non-SAP system in your company into the SAP System. Assume, for example, that data collection in some areas of your company is still performed by a non-SAP system. You can still consolidate all of your data in the SAP System by exporting the data from the other system and reading it into the SAP System with batch input.
You can also use batch input to transfer data between two R/3 Systems. However, there are more direct methods for doing this, such as RFC (remote function calls).
84 What has to be done to the packed fields before submitting to a BDC session?
Declare these fields in the internal table as characters and the length of the field should be same as the field length of the field's data element. This internal table is used to hold the data fetched from the sequential file using WS-upload function module
What is LSMW
The LSMW is a cross-application component (CA) of the SAP R/3 System.
The tool has interfaces with the Data Transfer Center and with batch input and direct input processing as well as standard interfaces BAPI and IDoc in R/3.
The LSMW comprises the following main functions:
Read data (legacy data in spreadsheet tables and/or sequential files).
Function Read data replaces and enhances functions Spreadsheet interface and Host interface of LSMW version 1.0. You can use any combination out of PC and server files now.
Convert data (from the source into the target format).
Import data (to the database used by the R/3 application).
TCODE - LSMW
Jun 19, 2009
SAP ABAP T-codes

S001 ABAP/4 Development Weorkbench.
SO01 Business Workflow
S002 System Administration.
SA38 Execute a program.
SCAT Computer Aided Test Tool
SCU0 Compare Tables
SE01 Old Transport & Corrections screen
SE03 Groups together most of the tools that you need for doing transports. In total, more than 20 tools can be reached from this one transaction.
SE09 Workbench Organizer
SE10 New Transport & Correction screen
SE11 ABAP/4 Dictionary Maintenance SE12 ABAP/4 Dictionary Display SE13 Maintain Technical Settings (Tables)
SE12 Dictionary: Initial Screen - enter object name.
SE13 Access tables in ABAP/4 Dictionary.
SE14 Utilities for Dictionary Tables
SE15 ABAP/4 Repository Information System
SE16 Data Browser: Initial Screen.
SE16N Table Browser (the N stands for New, it replaces SE16).
SE17 General Table Display
SE24 Class Builder
SE30 ABAP/4 Runtime Analysis
SE32 ABAP/4 Text Element Maintenance
SE35 ABAP/4 Dialog Modules
SE36 ABAP/4: Logical Databases
SE37 ABAP/4 Function Modules
SE38 ABAP Editor
SE39 Splitscreen Editor: Program Compare
SE41 Menu Painter
SE43 Maintain Area Menu
SE48 Show program call hierarchy. Very useful to see the overall structure of a program.
SE49 Table manipulation. Show what tables are behind a transaction code.
SE51 Screen Painter: Initial Screen.
SE54 Generate View Maintenance Module
SE61 R/3 Documentation
SE62 Industry utilities
SE63 Translation
SE64 Terminology
SE65 R/3 document. short text statistics SE66 R/3 Documentation Statistics (Test!)
SE68 Translation Administration
SE71 SAPscript layout set
SE71 SAPScript Layouts Create/Change
SE72 SAPscript styles
SE73 SAPscript font maintenance (revised)
SE74 SAPscript format conversion
SE75 SAPscript Settings
SE76 SAPscript Translation Layout Sets
SE77 SAPscript Translation Styles
SE80 ABAP/4 Development Workbench
SE81 SAP Application Hierarchy
SE82 Customer Application Hierarchy
SE83 Reuse Library. Provided by Smiho Mathew.
SE84 ABAP/4 Repository Information System
SE85 ABAP/4 Dictionary Information System
SE86 ABAP/4 Repository Information System
SE87 Data Modeler Information System
SE88 Development Coordination Info System
SE91 Maintain Messages
SE92 Maintain system log messages
SE93 Maintain Transaction.
SEARCH_SAP_MENU From the SAP Easy Access screen, type it in the command field and you will be able to search the standard SAP menu for transaction codes / keywords. It will return the nodes to follow for you.
SEU Object Browser
SHD0 Transaction variant maintenance
SM04 Overview of Users (cancel/delete sessions)
SM12 Lock table entries (unlock locked tables)
SM21 View the system log, very useful when you get a short dump. Provides much more info than short dump
SM30 Maintain Table Views.
SM31 Table Maintenance
SM32 Table maintenance
SM33 Display Table Parameter ID TAB
SM35 View Batch Input Sessions
SM37 View background jobs
SM50 Process Overview.
SM51 Delete jobs from system (BDC)
SM62 Display/Maintain events in SAP, also use function BP_EVENT_RAISE
SMEN Display the menu path to get to a transaction
SMOD Transactions for processing/editing/activating new customer enhancements.
CMOD Transactions for processing/editing/activating new customer enhancements.
SNRO Object browser for number range maintenance.
SPRO Start SAP IMG (Implementation Guide).
SQ00 ABAP/4 Query: Start Queries
SQ01 ABAP/4 Query: Maintain Queries
SQ02 ABAP/4 Query: Maintain Funct. Areas
SQ03 ABAP/4 Query: Maintain User Groups
SQ07 ABAP/4 Query: Language Comparison
ST05 Trace SQL Database Requests.
ST22 ABAP Dump analysis
SU53 Display Authorization Values for User.
WEDI EDI Menu. IDOC and EDI base.
WE02 Display an IDOC
WE07 IDOC Statistics
SAP BASIS T-Codes

SAP BASIS T-Codes
AL11 Display SAP Directories
BD54 Maintain Logical Systems
OSS1 Logon to Online Service System
SALE IMG Application Link Enabling
SARA Archive Management
SCC3 Copy Analysis Log
SCC4 Client Administration
SCC5 Client Delete
SCC7 Client Import Post-Processing
SCC8 Client Export
SCC9 Remote client copy
SCCL Local Client Copy
SCU0 Customizing Cross-System Viewer
SICK Installation Check
SM01 Lock Transactions
SM02 System Messages
SM04 User Overview
SM12 Display and Delete Locks
SM13 Display Update Records
SM14 Update Program Administration
SM21 System Log
SM35 Batch Input Monitoring
SM50 Work Process Overview
SM51 List of SAP Servers
SM56 Number Range Buffer
SM58 Asynchronous RFC Error Log
SM59 RFC Destinations (Display/Maintain)
SM66 System Wide Work Process Overview
SAINT SAP Add-on Installation Tool
SPAM SAP Patch Manager (SPAM)
SPAU Display modified DE objects
SPDD Display modified DDIC objects
ST11 Display Developer Traces
ST22 ABAP/4 Runtime Error Analysis
SU56 Analyze User Buffer
Alert Monitoring
AL01 SAP Alert Monitor
AL02 Database alert monitor
AL04 Monitor call distribution
AL05 Monitor current workload
AL16 Local Alert Monitor for Operat.Syst.
AL18 Local File System Monitor
RZ20 CCMS Monitoring
Configuration
FILE Cross-Client File Names/Paths
RZ04 Maintain Operation Modes and Instances
RZ10 Maintenance of Profile Parameters
RZ11 Profile parameter maintenance
SE93 Maintain Transaction Codes
SM63 Display/Maintain Operating Mode Sets
SPRO Customizing: Initial Screen
SWU3 Consistency check: Customizing
Database Administration
DB01 Analyze exclusive lockwaits
DB02 Analyze tables and indexes
DB12 DB Backup Monitor
DB13 DBA Planning Calendar
DB15 Data Archiving: Database Tables
Jobs
SM36 Define Background Job
SM37 Background Job Overview
SM39 Job Analysis
SM49 Execute External OS commands
SM62 Maintain Events
SM64 Release of an Event
SM65 Background Processing Analysis Tool
SM69 Maintain External OS
Monitoring
AL08 Current Active Users
OS01 LAN check with ping
RZ01 Job Scheduling Monitor
RZ03 Presentation, Control SAP Instances
ST01 System Trace
ST02 Setups/Tune Buffers
ST04 Select DB activities
ST05 Performance trace
ST06 Operating System Monitor
ST10 Table call statistics
ST03 Performance, SAP Statistics, Workload
ST07 Application monitor
STAT Local transaction statistics
STUN Performance Monitoring (not available in R/3 4.6x)
Spool
SP01 Output Controller
SP11 TemSe directory
SP12 TemSe Administration
SPAD Spool Administration
Transports
SCC1 Client Copy - Special Selections
SE01 Transport Organizer
SE06 Set Up Workbench Organizer
SE07 CTS Status Display
SE09 Workbench Organizer
SE10 Customizing Organizer
SE11 ABAP/4 Dictionary Maintenance
SE16 Data Browser
SE80 Repository Browser
SM30 Call View Maintenance
SM31 Table Maintenance
STMS Transport Management System
User Administration
PFCG Profile Generator (Activity Group Maintenance)
PFUD User Master Data Reconciliation
SU01 User Maintenance
SU01D User Display
SU02 Maintain Authorization Profiles
SU03 Maintain Authorizations
SU05 Maintain Internet users
SU10 User Mass Maintenance
SMLG Maintain Logon Group
SUPC Profiles for activity groups
SUIM Infosystem Authorizations
Other Transactions
AL22 Dependent objects display
BAOV Add-On Version Information
SA38 ABAP reporting
SE38 ABAP Editor
HIER Internal Application Component Hierarchy Maintenance
ICON Display Icons
WEDI IDoc and EDI Basis
WE02 IDoc display
WE07 IDoc statistics
WE20 Partner profiles
WE21 Port definition
WE46 IDoc administration
WE47 Status Maintenance
$TAB Refreshes the table buffers
$SYNC Refreshes all buffers, except the program buffer
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
How to change Transport request from Released to Modifiable
Step 1: Go to SE38 – Execute Program RDDIT076. Step 2: Give your released requests number and execute again. Step 3: After executing, yo...
-
Links to various helpful posts on SAP PI on SCN n other sites. Process Integration (PI) & SOA Middleware-SCN http://scn.sap.com/comm...
-
Function module that will take any internal table as input, convert in to XLS format and send out emails with the attachment. Add the...
-
Category : ABAP Programming Error Runtime Errors: READ_REPORT_LINE_TOO_LONG Except.: CX_SY_READ_SRC_LINE_TOO_LONG Detail explanati...



